Botanical Name: Malva sylvestris
Family: Malvaceae (Mallow family)
Common Names:
-
English: High Mallow, Common Mallow, Tall Mallow
-
Hindi: Gurchanti, Socholi
-
Kannada: Sanna Bindige Gida, Seeme Bende
-
Marathi: Kubaajee
-
Urdu: Khubbazi, Tukhm-e-Khubbazi, Gul-e-Khubazi, Gul-e-Khair
Description
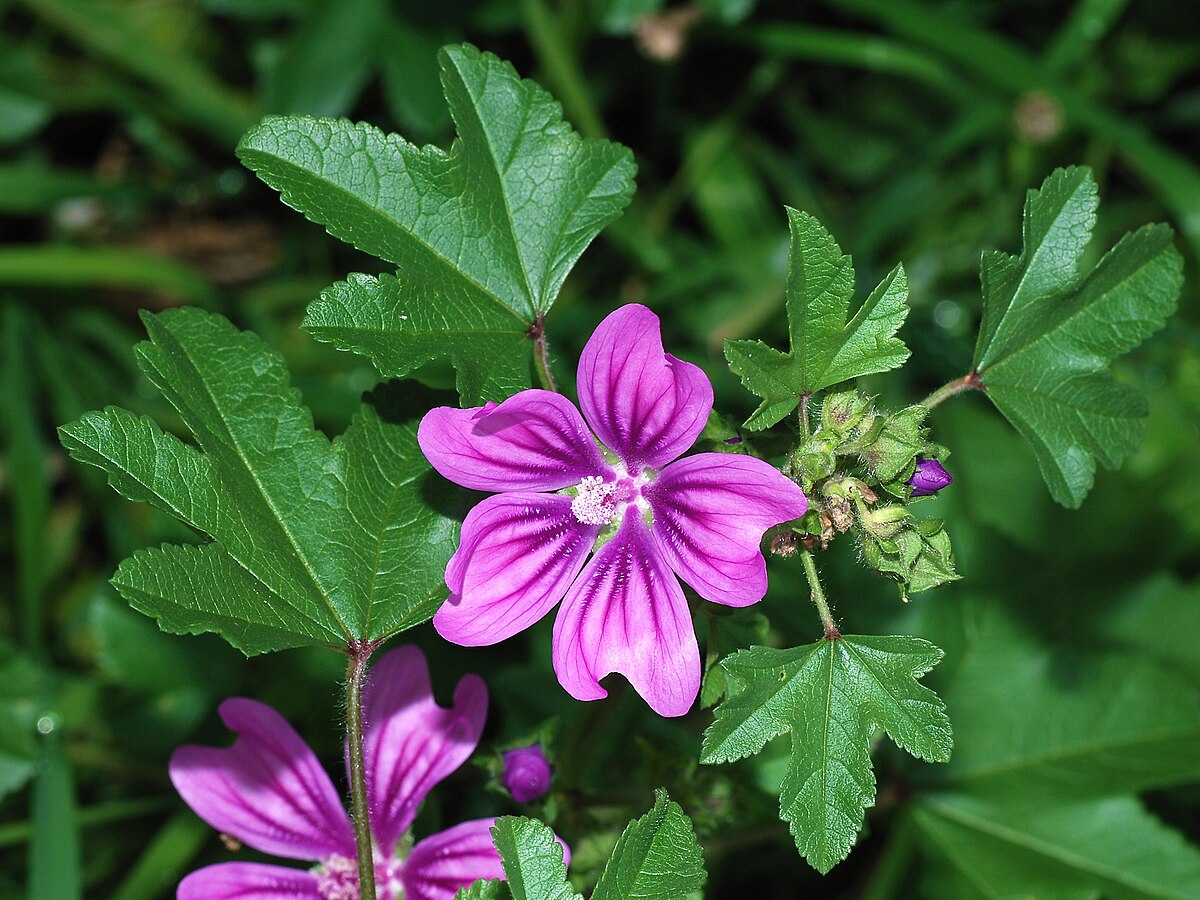
Malva sylvestris, popularly known as High Mallow, is a spreading perennial herb that typically grows up to 3 feet in height in gardens, though it can reach taller heights in the wild.
Key Features:
-
Stems: Straight or prostrate, branched, with soft fine hairs or sometimes hairless.
-
Leaves: Alternately arranged, deep green, soft, and downy. They are roundish with 3-7 shallow lobes, measuring 2-5 cm across.
-
Flowers: Large, numerous, purple in color, and appear in clusters of 2-4 in leaf axils. Each flower has five petals with a wrinkled appearance and distinctive fringed margins.
-
Seeds: Known as ‘cheeses’ due to their wheel-like shape, brownish when ripe, about 2.5 mm wide and 5-7 mm in diameter.
Habitat:
Native to Western Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia, it is commonly found in woodlands, sunny garden edges, hedgerows, and dappled shaded areas. In India, it grows in the Himalayas from Kashmir to Kumaon at elevations up to 2400 meters.
Parts Used
-
Flowers
-
Leaves (herbs)
Principal Constituents
The plant is rich in mucilage, primarily made of nine sugar residues including Galacturonic acid (GalA) and Glucuronic acid (GlcA). It also contains Scopoletin, a known anti-inflammatory agent.
Medicinal Uses
High Mallow has been valued in traditional herbal medicine since ancient Roman times for its wide range of therapeutic benefits:
Internal Uses:
-
Demulcent: Soothes irritations in the throat, chest, and digestive tract.
-
Expectorant: Helps in relieving coughs, bronchial congestion, and chest ailments (especially when combined with Eucalyptus).
-
Laxative: Gentle enough for children.
-
Diuretic: Supports kidney and urinary health.
External Uses:
-
Emollient & Poultice: Crushed leaves or flowers applied to bruises, skin inflammations, insect bites, and minor wounds.
-
Natural Cataplasm: Relieves external inflammatory conditions.
Other Uses:
-
Leaves and flowers can be eaten raw in salads or cooked as vegetables.
-
Unripe seed pods, known as 'cheeses,' are edible.
-
Traditionally used for treating whooping cough, kidney problems, and skin conditions.
-
Officially recognized in French and Swiss pharmacopoeias.
Harvesting & Preparation
-
Leaves: Freshly used or dried in spring for later use.
-
Flowers: Harvested in summer and dried for medicinal preparations.
Conclusion
Malva sylvestris is a gentle yet powerful medicinal herb with soothing, anti-inflammatory, and expectorant properties. Its versatility in both dietary and medicinal use, alongside its historical importance, makes it a valuable plant in traditional herbal medicine and home remedies.
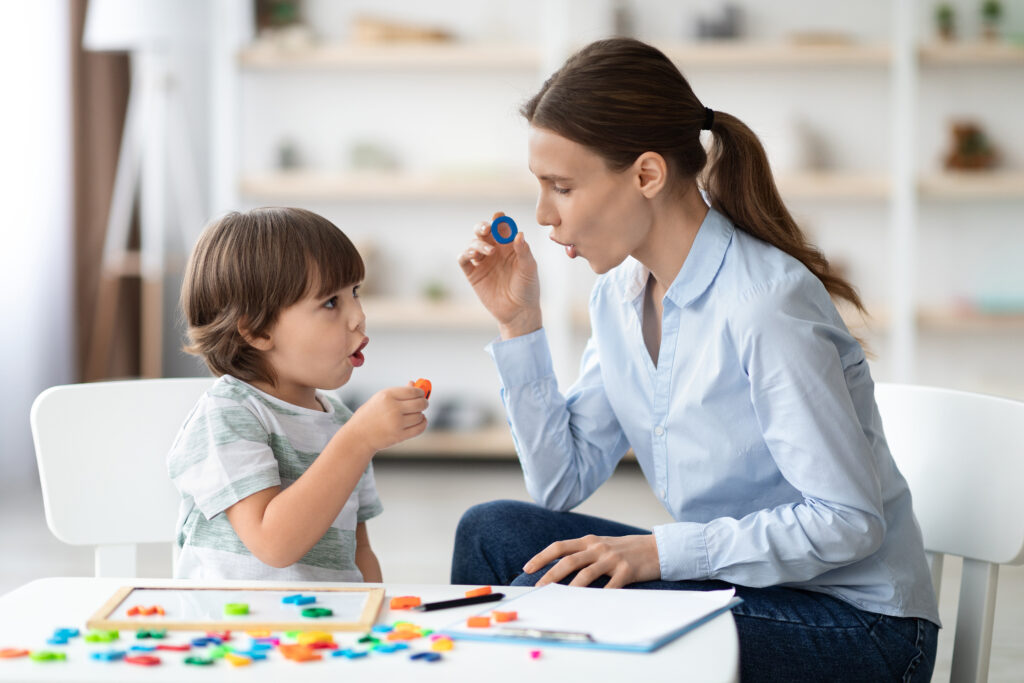
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...