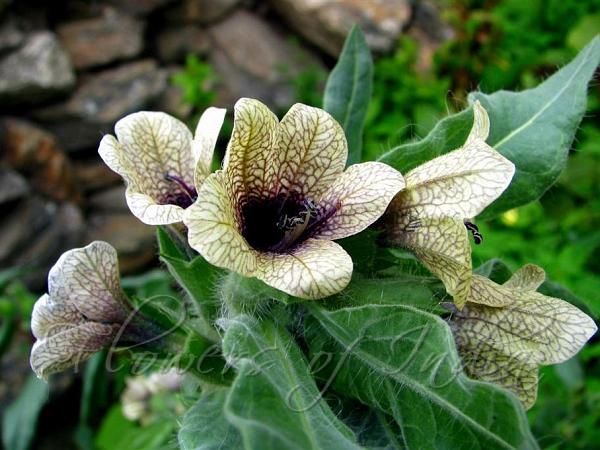
Family: Solanaceae
Common Names: Stinking Nightshade, Black Henbane, Common Henbane, Hog’s Bean, Jupiter’s Bean, Symphonica, Cassilata.
Parts Used:
-
Fresh leaves
-
Flowering tops and branches
-
Seeds
Traditional and Medicinal Uses:
Hyoscyamus niger is a historically valued medicinal plant known for its anodyne, narcotic, and mydriatic properties. Its therapeutic effects closely resemble those of Belladonna and Stramonium, though it tends to act more mildly.
Internal Uses:
-
Sedative for nervous disorders, including hysteria, asthma, and whooping cough.
-
Substituted for opium in cases where opium is unsuitable.
-
Relieves spasms in the urinary tract and counters the griping effect of purgatives.
-
Used in insomnia, especially where opium is contraindicated.
-
In small, repeated doses, it produces a calming effect, promoting sleep without the digestive disturbances often associated with opium.
External Uses:
-
Poultices and liniments for painful, rheumatic conditions.
-
Relieves toothache when powdered seeds or their smoke are applied.
-
Suppositories prepared from seeds are used in painful uterine conditions.
-
Dilute extracts applied to the eye cause pupil dilation (mydriasis) before operations or to ease internal inflammation.
Therapeutic Properties:
-
Anodyne: Relieves pain
-
Narcotic: Induces sleep and reduces mental agitation
-
Antispasmodic: Alleviates spasms in involuntary muscles
-
Hypnotic: Promotes sleep
-
Mild Diuretic: Increases urine output
-
Alterative, Purgative, Antiperiodic: Traditional uses in treating piles, skin diseases, dysentery, rheumatism, leprosy, bronchial afflictions, and liver issues.
Key Constituents:
-
Hyoscine (Scopolamine): The main active alkaloid, powerfully sedative — used in minuscule doses (1/200 to 1/70 grain of its Hydrobromate form).
-
Small amounts of Atropine (less excitatory than Belladonna)
-
Other alkaloids used primarily for their narcotic and sedative effects.
Precautions:
In toxic doses, Henbane causes dim vision, faintness, delirium, and potentially death. It is classified under Table I of the Poisons Schedule in many pharmacopeias and should be used under strict professional supervision.
Modern Medical Applications:
-
Treatment of acute mania and delirium tremens in psychiatry (asylums).
-
Used in Twilight Sleep (a controlled, pain-free sedation method) due to its brain and spine sedative action.
-
Ingredients from Henbane are also employed in compound liniments for external pain relief.
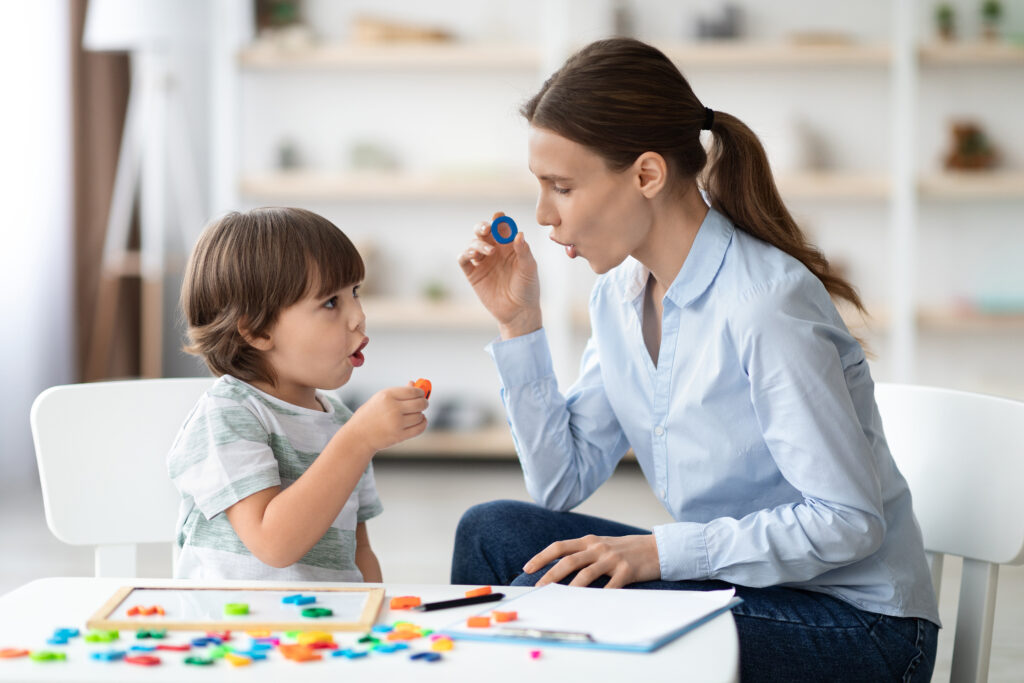
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...