Botanical Name: Gentiana lutea L.
Family: Gentianaceae
Common Names: Yellow Gentian, Bitter Root, Bitterwort, Enzian, Centiyane, Genciana
Parts Used: Dried rhizome and root
Habitat: Native to the mountainous regions of central and southern Europe
Traditional and Medicinal Uses
Gentiana lutea has a rich history in traditional European medicine, primarily recognized for its intensely bitter root. This bitterness stimulates digestive secretions, making it valuable for:
-
Digestive Disorders: Effective in treating indigestion, dyspepsia, and loss of appetite.
-
Liver and Gallbladder Health: Stimulates bile production, aiding in liver function.
-
General Debility: Acts as a tonic in cases of exhaustion from chronic illnesses.
-
Anemia and Fevers: Traditionally used to combat anemia and reduce fevers.
-
Antidote: Historically considered an antidote for certain poisons.
The root is often combined with purgatives to mitigate their weakening effects on the body.
Active Constituents
Gentiana lutea's therapeutic properties are attributed to its diverse phytochemical composition:
-
Secoiridoid Glycosides:
-
Amarogentin: One of the most bitter natural compounds, used as a standard for measuring bitterness.
-
Gentiopicrin (Gentiopicroside): Stimulates digestive secretions and may protect the liver.
-
-
Xanthones:
-
Gentisin and Isogentisin: Possess antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
-
-
Alkaloids:
-
Gentianine: Exhibits anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
-
-
Phenolic Acids:
-
Gentisic, Caffeic, Protocatechuic, Syringic, and Sinapic Acids: Contribute to the plant's antioxidant activity.
-
Therapeutic Actions
-
Bitter Tonic: Enhances appetite and digestion.
-
Cholagogue: Promotes bile flow.
-
Anthelmintic: Expels intestinal worms.
-
Antiseptic: Prevents infection.
-
Emmenagogue: Stimulates menstrual flow.
-
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant: Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress.
-
Antimicrobial: Fights against microbial infections.
Precautions
-
Gastrointestinal Conditions: Not recommended for individuals with gastric or duodenal ulcers, as it may exacerbate symptoms.
-
Hypertension: Use with caution in individuals with high blood pressure.
-
Pregnancy: Due to its emmenagogue properties, it should be avoided during pregnancy.
Historical Context
The name "Gentian" is derived from Gentius, an Illyrian king who, according to legend, discovered the plant's medicinal properties. Before the widespread use of hops, Gentiana lutea was utilized in brewing for its bitter flavor. It remains a key ingredient in traditional bitters, such as Angostura.
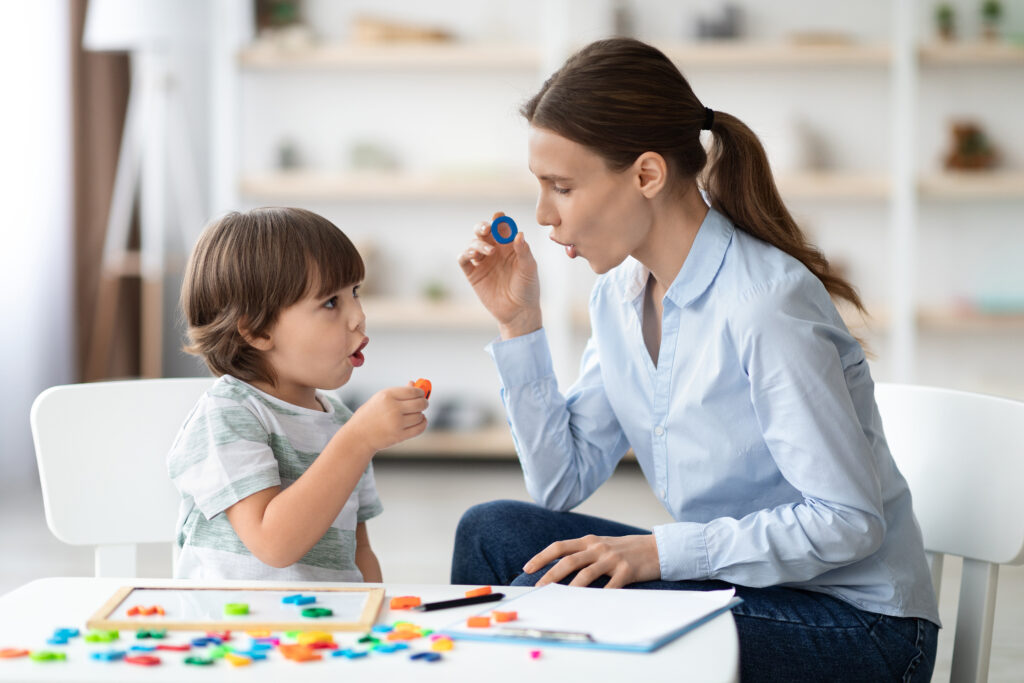
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...