Synonyms: Genista andreana, Genista scoparia, Sarothamnus scoparius, Sarothamnus vulgaris, Spartium scoparium, Cytisus scoparius (L.)
Common Names:
Broomtops, Common Broom, European Broom, Irish Broom, Scottish Broom, Greenweed, Greenwood, Dyers' Broom, Woad-waxen, Wood-waxen, Genet des Teinturiers, F. „Berginster.
Family: Fabaceae (Legume family) — sometimes placed under Papilionaceae.
Part Used: Whole plant (primarily flowering twigs)
Habitat: Native to the Mediterranean regions, Canary Islands, Western Asia, and Britain; also well-established in the United States.
Description
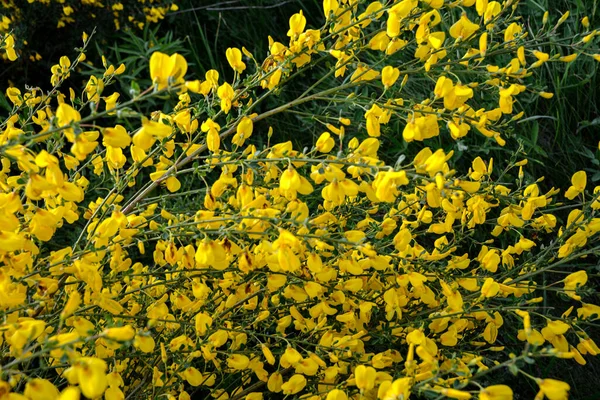
Genista scoparia is a small, tufted shrub with slender, erect, and branched green stems reaching 1–2 feet in height. The stems are smooth or slightly hairy and lack spines. The leaves are narrow, spear-shaped, alternating along the stem, and measure about ½ to 1 inch in length. Bright yellow flowers appear in short racemes, making it popular even for greenhouse cultivation in some regions.
Constituents
-
Scopnarine: Starry, yellow crystals, soluble in boiling water and alcohol.
-
Sparteine: An organic base with strong narcotic and vasoactive properties.
This plant is also notable as the original source of the isoflavone genistein, discovered in 1899, after which the compound is named.
Medicinal Properties & Uses
-
Actions: Diuretic, cathartic (mild purgative), emetic, stimulant, and vaso-constrictor.
-
Central Nervous System: Stimulates the CNS; its effects are comparable to nicotine.
-
Blood Pressure: Increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels — should be avoided by hypertensive patients.
Traditional Medicinal Uses:
-
Flowers & Seeds: Historically used as purgatives and diuretics.
-
Tea/Infusion: Acts as a mild laxative and has been recommended for gravel (urinary calculi), kidney stones, and dropsy.
-
External Applications: Tinctures and extracts have been used to treat herpes, tetters, scrofulous tumors, cold abscesses, and chronic skin ailments.
-
Dropsy & Albuminuria: Decoctions and infusions are valued remedies.
-
Historical Ointments: In the 14th century, it was an ingredient in Unguentum geneste, reputedly "good for all cold gouts."
-
Poultices: Applied for cold abscesses and broken limbs.
-
Ashes: Used to create alkaline salts, once prescribed for dropsy and other conditions.
Historical Notes
Greek physician Dioscorides and Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder documented the purgative and diuretic properties of Genista scoparia. It has a long-standing history in European folk medicine for treating urinary disorders, dropsy, and rheumatism.
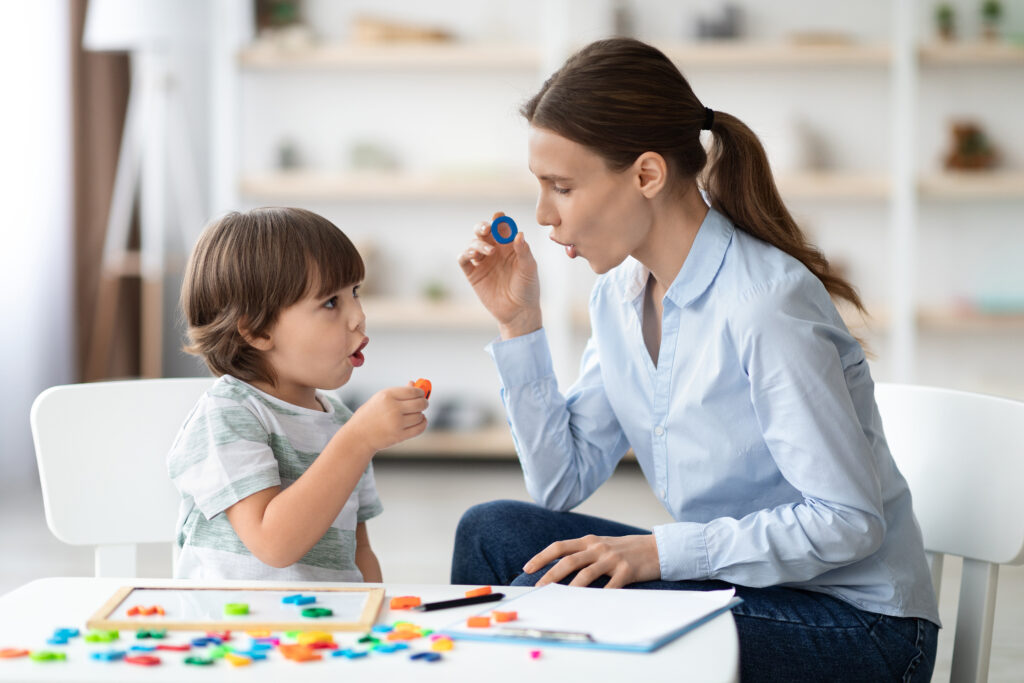
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
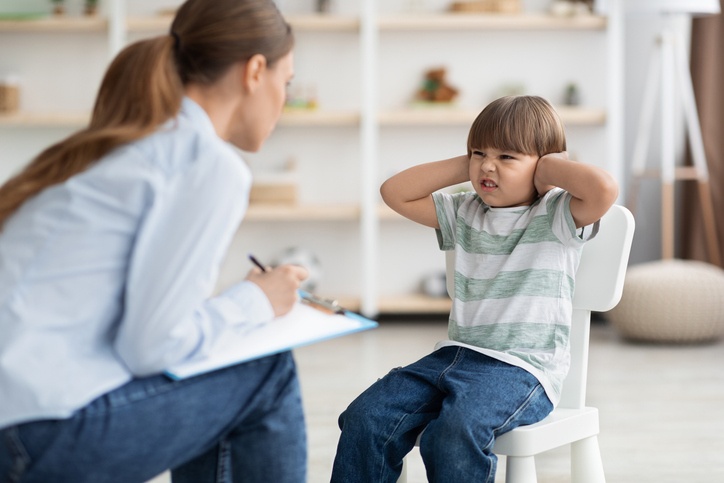
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...