Family: Celastraceae
Common Names: Indian Arrowroot, Burning Bush, Spindle Tree, Eastern Wahoo
Parts Used: Bark, Root Bark
Introduction
Euonymus atropurpureus, commonly known as the Eastern Wahoo or Burning Bush, is a deciduous shrub native to the Midwestern United States, with its natural range extending from southern Ontario to northern Florida and Texas. This plant is recognized both for its ornamental appeal — especially its bright red foliage in autumn — and its medicinal properties.
Botanical Description
-
Height: Grows up to 8 meters tall.
-
Bark: Gray, smooth, and lightly fissured.
-
Twigs: Slender, dark purplish-brown, occasionally four-angled or slightly winged.
-
Leaves: Opposite, elliptical, 8.5–11.3 cm long and 3.2–5.5 cm broad, finely serrated, green above and paler with fine hairs beneath. In autumn, the leaves turn vivid red.
-
Flowers: Small, bisexual, about 10–12 mm in diameter, with four greenish sepals, four brown-purple petals, and four stamens. These appear in small axillary clusters (cymes) around June.
-
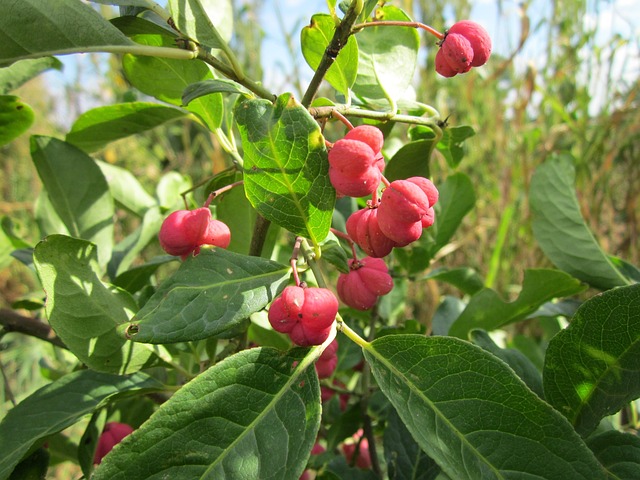
Fruit: Smooth, reddish to pink, four-lobed capsules up to 17 mm in diameter. Each lobe contains a single seed, enveloped in a fleshy red aril. These attractive fruits have earned the plant the nickname Hearts Bursting with Love. While poisonous to humans, the fruits are favored by birds that help disperse the seeds.
Habitat:
It typically thrives in moist soils of low meadows, stream banks, open woodlands, prairies, valleys, and forest edges.
Medicinal Uses
Euonymus atropurpureus has a long history in Native American and early pioneer medicine. Today, it is still valued in herbalism, though caution is required due to its toxicity.
-
Gallbladder and Liver Health: Considered a gallbladder remedy with both laxative and diuretic effects. Particularly effective in addressing biliousness, liver congestion, and liver-related skin conditions like eczema.
-
Cardiac Benefits: The bark and root contain digitoxin-like compounds, offering a digitalis-like action on the heart. Traditionally used for heart conditions, but only under professional supervision.
-
Digestive Support:
-
In small doses, it stimulates appetite.
-
In larger doses, it acts as a purgative, irritating the intestines.
-
Used for constipation and related digestive issues.
-
-
Antimalarial Remedy: A tea made from the bark was historically used to treat malaria.
-
Women’s Health: The root tea was traditionally administered for uterine prolapse, vomiting of blood, painful urination, and abdominal discomfort.
-
Skin and Scalp Care:
-
The powdered bark was applied to the scalp to eliminate dandruff.
-
Also applied for skin issues arising from liver and gallbladder dysfunction.
-
Note:
The bark is toxic and should only be used under qualified supervision. It is unsafe for pregnant or nursing women.
Additional Information
-
Soil Preferences: Tolerates sandy, loamy, and clay soils. Can grow in acidic, neutral, or alkaline conditions.
-
Light Requirements: Thrives in semi-shade or full sunlight.
-
Hardiness: Suitable for USDA Zone 4.
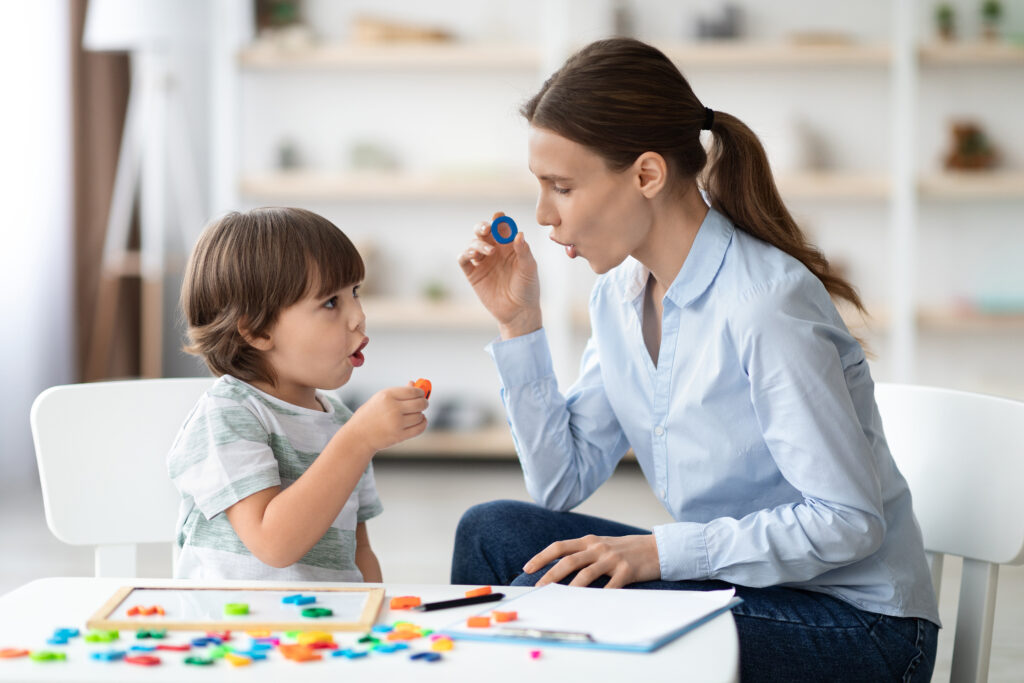
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
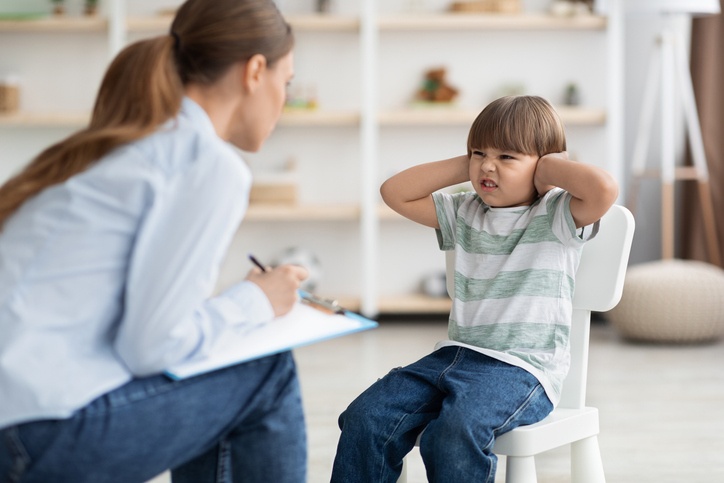
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
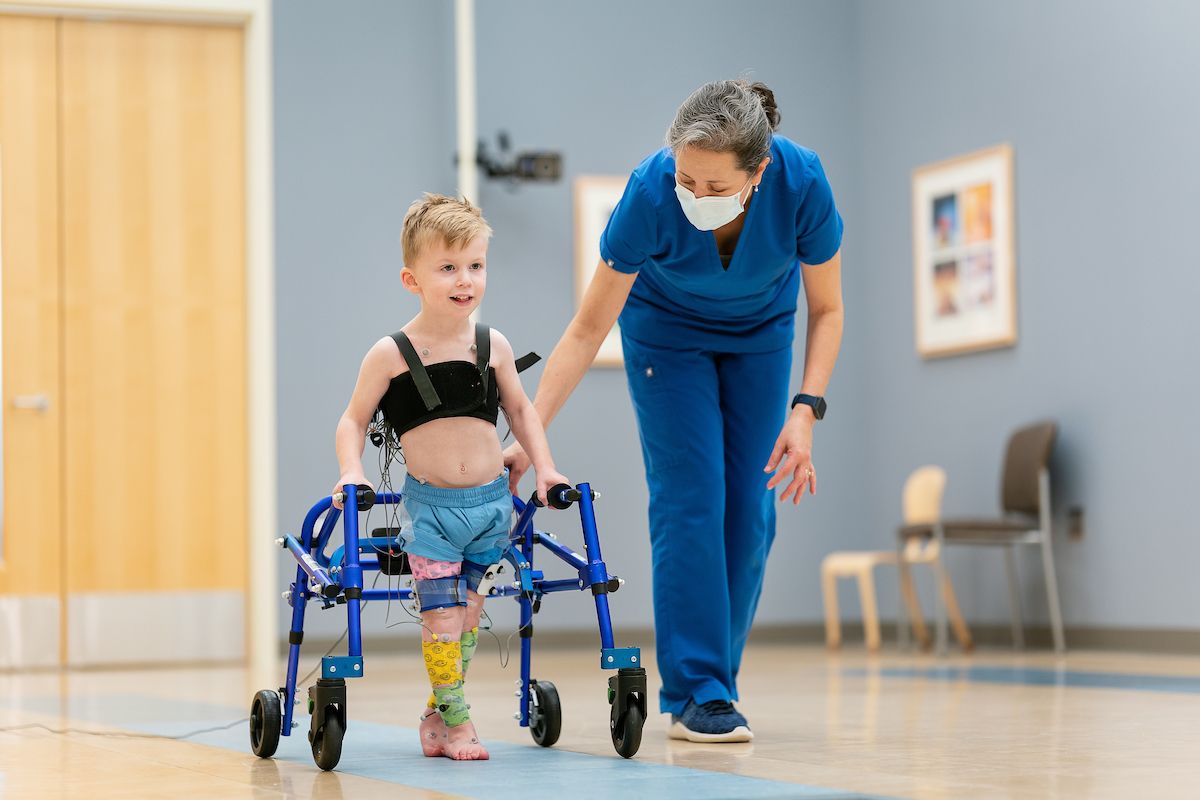
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
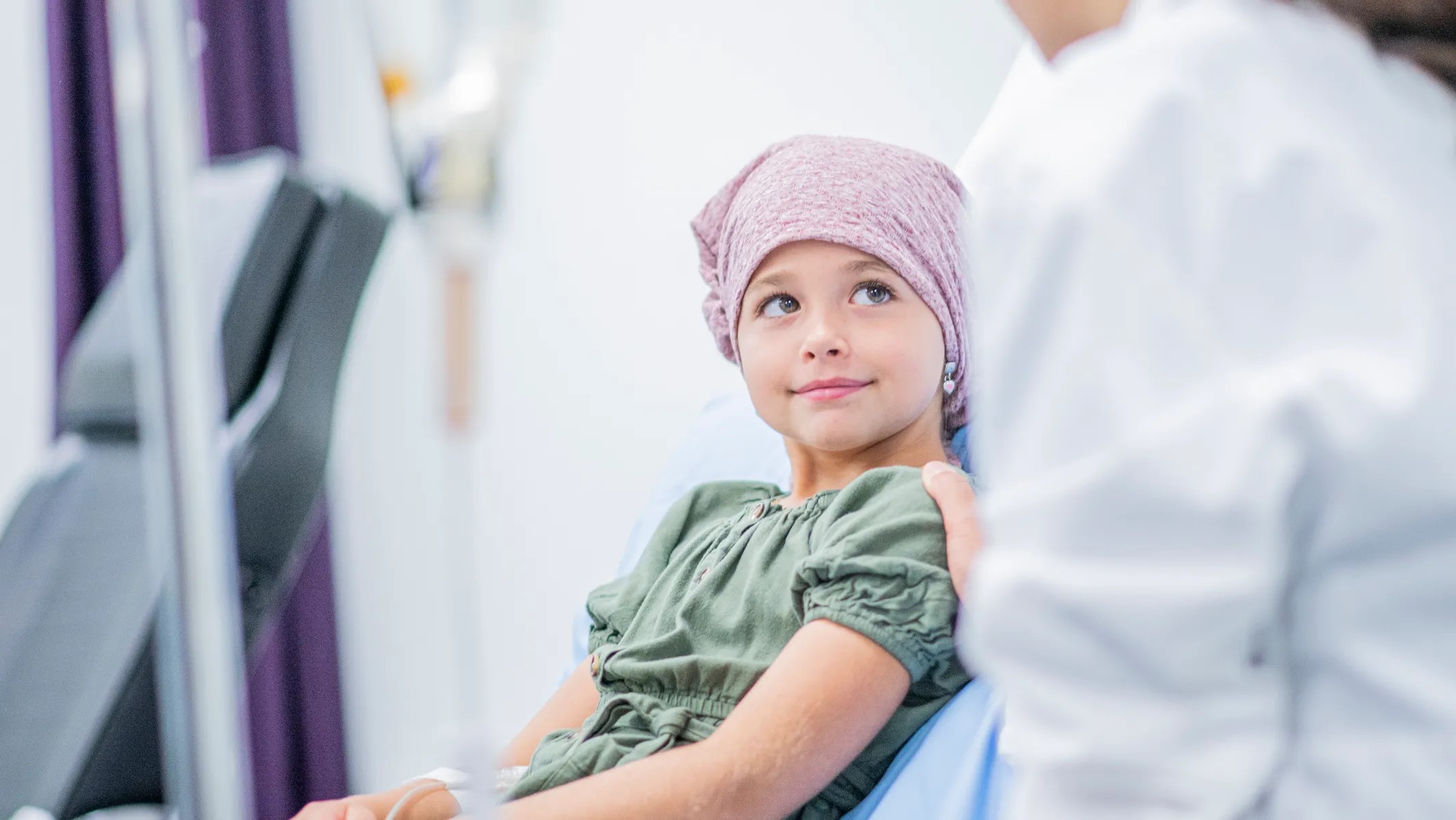
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...