Capsella bursa-pastoris, commonly called Shepherd’s Purse, is a small plant known for its tiny, purse-shaped seed pods. It belongs to the mustard family (Brassicaceae) and usually grows up to 50 cm tall.
Other names people call it:
-
Shepherd's Bag
-
Lady’s Purse
-
Witches’ Pouches
-
Case-weed
-
Pick-Pocket
-
Blindweed
-
Pepper-and-Salt
-
Poor Man's Parmacettie
-
Mother’s Heart, and many more.
Part Used:
The whole plant (except the root) is used for medicinal purposes.
Where It’s Found:
Originally from Eastern Europe and Asia Minor, Shepherd's Purse has now spread all over the world, especially in cooler regions like Britain, North America, China, the Mediterranean, and North Africa. It’s commonly seen growing by roadsides, in fields, and open areas.
What It Looks Like:
-
Stems: Up to 50 cm tall, straight, and may have branches.
-
Leaves: The leaves at the base are divided into small parts, while the upper ones are narrow and clasp the stem.
-
Flowers: Tiny white flowers with four petals, appearing in clusters at the top.
-
Fruits: Small, flat, heart-shaped pods that look like little purses.
-
Flowering Time: From March to November.
History:
It gets its name because the seed pods look like the old leather purses people once carried. In Ireland, it was nicknamed Clappedepouch, after the lepers who begged at roadsides. The plant traveled with European settlers and spread wherever they went, including America.
Chemical Components:
Shepherd’s Purse contains:
-
Saponins, Oils, Flavonoids, Resins, Tannins, and Essential oils
-
Important nutrients like Vitamin C, B1, B2, A (Beta-carotene), Vitamin K
-
Minerals like Calcium, Potassium, Phosphorus, Iron
-
Other compounds like Acetylcholine, Diosmine, Rutin
Medicinal Uses:
Shepherd’s Purse is a very important medicinal plant, known for:
-
Stopping Bleeding (Haemostatic)
-
Astringent (tightens tissues)
-
Anti-inflammatory
-
Diuretic (increases urine flow)
-
Helps with menstrual issues
-
Improves blood circulation
-
Fights scurvy (Vitamin C deficiency)
How it’s used: The whole plant (except roots) is used, either fresh or dried, usually made into a tea or infusion. Fresh plant works better because drying reduces its healing power.
Medicinal Benefits:
-
Controls internal bleeding: From the stomach, lungs, kidneys, and uterus.
-
Helps with heavy menstrual bleeding
-
Treats diarrhea and dysentery
-
Reduces inflammation and swelling in wounds
-
Good for bladder infections and urinary issues
-
Used on bruises, muscle strains, and joint pain
-
Helps ease nosebleeds when the juice is applied on cotton
During World War I, when other medicines were unavailable, a liquid extract of Shepherd’s Purse was used in Germany to stop bleeding.
Famous Herbal Mentions:
-
Culpepper (a famous herbalist) recommended it for stopping wounds from bleeding and treating jaundice.
-
Dr. Ellingwood praised its ability to soothe irritation in the urinary tract, treat excessive menstrual bleeding, and ease kidney problems.
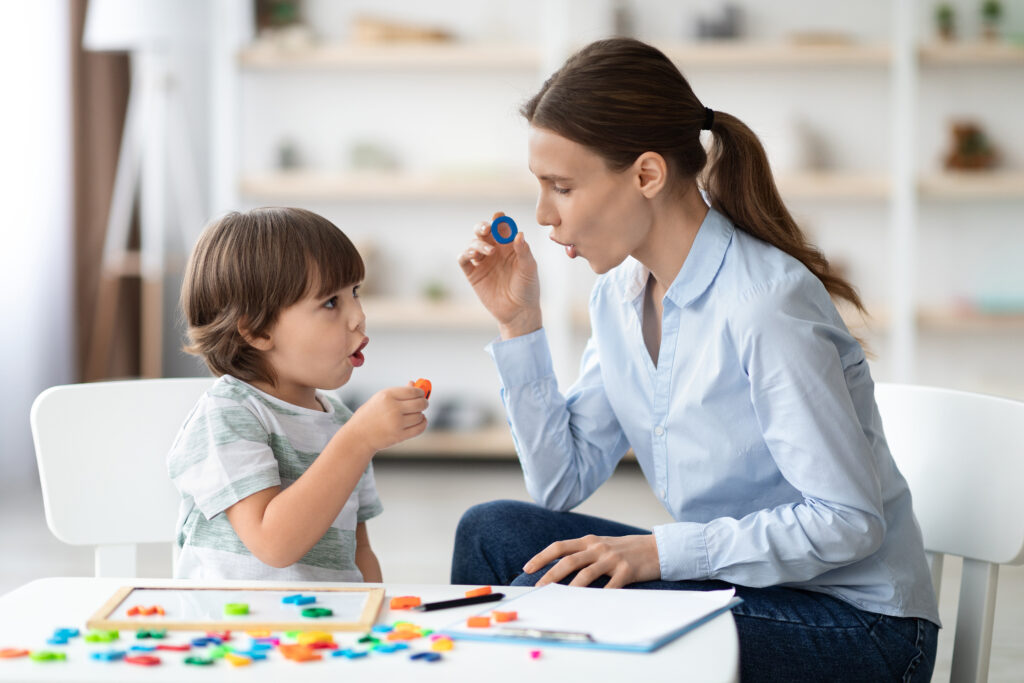
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
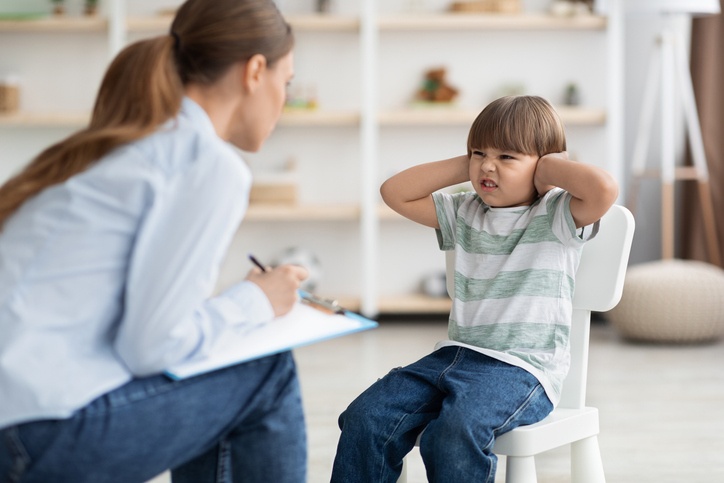
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...