Classification: -
Kingdom: Plantae
Division: Angiosperms
Class: Eudicots
Order: Ranunculales
Family: Berberidaceae
Genus: Berberis
Species: Berberis vulgaris
Introduction:
Berberis vulgaris, also known as barberry, is a deciduous spiny shrub which belongs to family Berberidaceae. This plant is native to Europe, North Africa and parts of Western Asia. It is cultivated in many temperate regions of the world. This plant has been used since ancient times for its therapeutic properties as well as its attractive appearance. Berberis vulgaris has a complex role in biodiversity as it provides food and shelter for wildlife.
Habit and Habitat:
In addition to its medical importance, Berberis vulgaris has ecological and agricultural significance. This plant grows both in the wild and under cultivation. The plant exhibits an erect, woody habit with numerous rigids, spreading branches. The genus Berberis has more than 450 species which are distributed throughout the temperate regions. The young branches of plant are yellowish to brown in color, while older stems become greyish or brown with age. Flowering occurs in late spring to early summer.
Berberis vulgaris is commonly found in open woodlands, forests, rocky slopes and grasslands. The species of the plant prefers well- drained soils and can grow in wide range of soil types including sandy, loamy and calcareous soil. The plant is well adapted to dry or moderately moist environment and can tolerate mild acidic to alkaline soil conditions.
Morphology and Anatomy:
Berberis vulgaris has distinctive morphological and anatomical features that have both ecological and medicinal significance. The plant typically grows to a height of 2-3 meters having spiny branches, small oval leaves, yellow flowers and bright red berries.
- The branches of the plant are slender shaped, forming a dense, compact structure.
- The leaves are simple, dark green in color, ovate to elliptic in shape, arranged in clusters on short shoots, while the spines are developed on long shoots.
- The flowers of the plant are small, yellow and hermaphroditic. These flowers later develop into oblong, bright red berries that are rich in organic acids and bioactive compounds.
- The fruit is oblong, bright red berry, containing one to three seeds. The berries are acidic in nature and are often used in traditional medicines.
Berberis vulgaris exhibits typical dicotyledonous anatomical features. It has certain distinctive characteristics related to its woody and medicinal nature. Its anatomy is well- developed in the stem, roots, and leaves that reflects its adaptation to a shrubby habit and temperate environments
In transverse section, the young stem of the plant is circular in shape. The outer epidermis consists of a single layer of compact cells covered by a thin cuticle to reduce water loss. Beneath the epidermis lies the cortex which mainly consists parenchymatous cells. The vascular tissues are arranged in a ring of collateral vascular bundles. Each bundle consists of xylem and phloem tissues. The leaf of the plant shows dorsiventral structure. The upper epidermis has thick cuticles which helps to reduce loss of water and lower epidermis contains numerous stomata. Roots of the plant exhibits a typical dicot structure with a well- defined epidermis, cortex, endodermis and central vascular cylinder.
Medicinal use:
Berberis vulgaris is most widely studied because of its ornamental value and medicinal properties. The berries are edible, though sour in taste which are traditionally used in herbal medicine and as a source of natural dyes. The extracts of the plant are used to treat eczema, rashes and minor infections. This plant possesses anti- inflammatory and antioxidant properties which is beneficial in conditions like arthritis, skin disorders and wound healing. It is also used to enhance general immunity and protect against infections. The fruits of the plant are acidic but can also be consumed as a tonic or in jams and syrups to improve appetite and digestion.
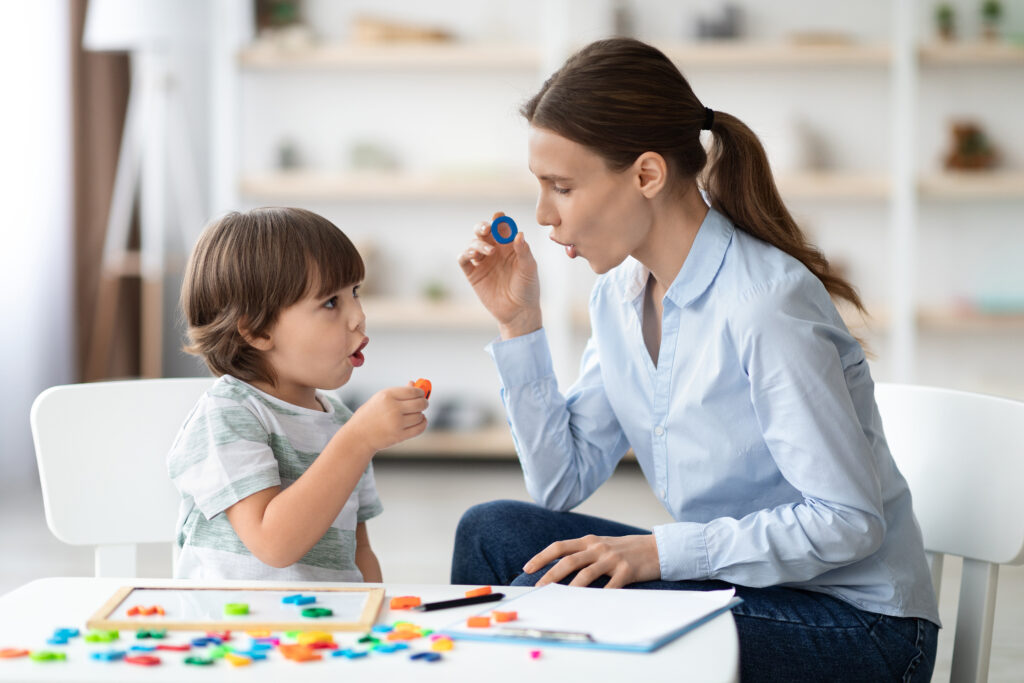
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
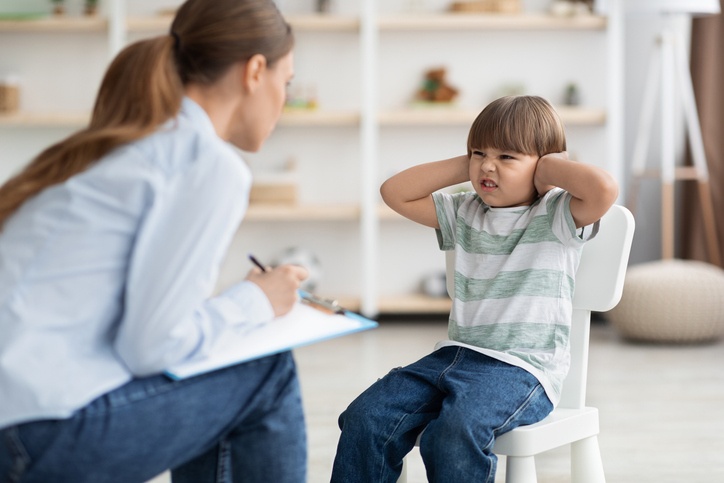
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...