Classification : -
Kingdom : Plantae
Class : Eudicots
Order : Malvales
Family : Malvaceae
Genus : Althaea
Species : Althaea officinalis
Introduction :
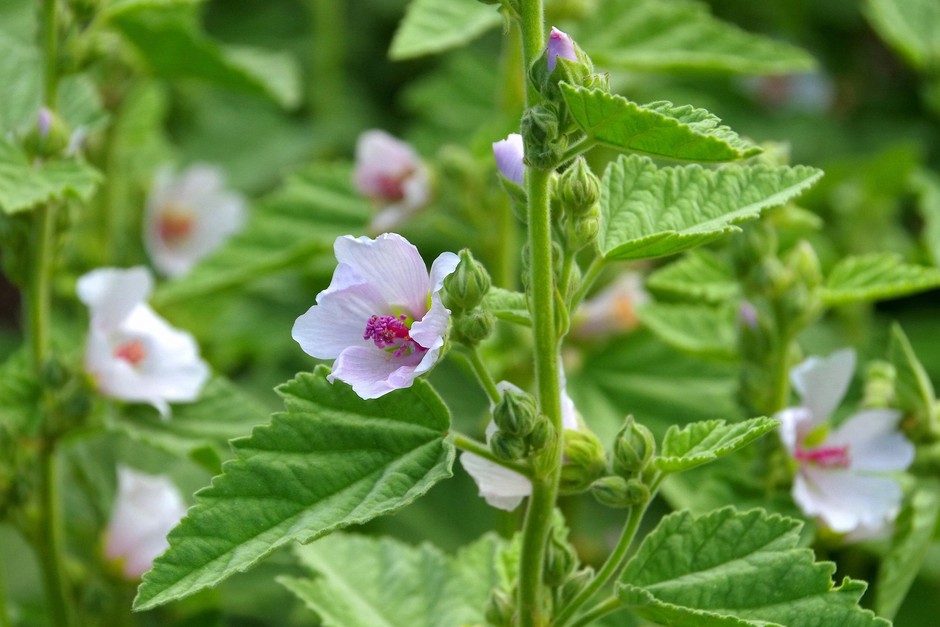
The name Althaea has been derived from the Greek word altho meaning “to heal” and is commonly known as marshmallow which is a perennial medicinal herb. It belongs to the Malvaceae family and has been used for thousands of years for its soothing, healing and protective properties. This plant has been long valued in traditional European and Middle Eastern regions. It can be easily recognized by its soft, velvety leaves and pale pink to white flowers that bloom during summer months.
Habit and Habitat :
Althaea plant is native to damp regions of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. This plant typically grows in marshy areas, river banks and moist meadows. It grows at an average height from 1-1.5 m tall having erect and soft pubescent stems. The plant is sometimes cultivated in gardens for medicinal and ornamental use. Flowering of the plant occurs in mid to late summer from May to November.
Morphology and Anatomy :
· The stem of Althaea officinalis is soft, erect, unbranched to sparingly branched, densely covered with fine, stellate hairs.
· Leaves of the plant are alternate, broadly ovate displaying three shallow lobes.
· Flowers of the plant are pale pink to whitish containing five petals.
· Fruits are disc- shaped schizocarps which are composed of numerous mericarps, arranged in a wheel- like pattern.
· Roots of the plant are thick, fleshy, white which is rich in mucilage containing parenchyma.
Medicinal Uses :
Althaea officinalis, is renowned for its medicinal and cultural significance. The roots, leaves and flowers of this plant are used in herbal preparations such as in tea, syrups and topical formulations. It is used to treat respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinary tract problems. This plant also helps to cure throat problems such as cough, sore throat with the help of original marshmallow sweet which is created by blending the plant’s mucilaginous extract with honey or sugar.
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...