Classification : -
Kingdom: Plantae
Class: Magnoliopsida
Order: Asterales
Family: Asteraceae
Genus: Anthemis
Species: Anthemis nobilis
Introduction :
Anthemis nobilis is a perennial herb commonly known as Roman chamomile. It is native to Western Europe and in Mediterranean regions. The plant has been cultivated for centuries for its fragrant flowers and soothing therapeutic properties. It has pleasant apple like aroma and attractive daisy like blooms which have been used in herbal remedies or household preparations since ancient times. This plant was highly recognized by Egyptians, Greeks and Romans for it’s calming, anti- inflammatory and restorative qualities. Anthemis nobilis belongs to Asteraceae family that includes daisies, sunflowers and asters.
Habit and Habitat :
Roman chamomile is low- growing which thrives in well- drained, sandy or loamy soils and prefers full sun to partial shade. The plant grows 10-30 cm tall having spreading habit due to its creeping stems which allow it to form dense ground covers. The stems are often slightly hairy with feathery leaves which gives it a delicate texture. During flowering season usually from late spring through summer Roman chamomile produces daisy- like flower heads with white ligulate petals surrounding a yellow central disc. The plant is evergreen and maintains its attractive appearance throughout the year.
Morphology and Anatomy :
Root system : Anthemis nobilis possesses fibrous root system having numerous fine branching roots that spread laterally just below the soil surface. The roots of plant allow efficient absorption of water in well- drained, often dry soils.
Stem : The stems of plant are herbaceous, slender and slightly hairy. Flowering stems of plant arise vertically from the creeping base which usually reach 10-30 cm in height.
Leaves : Leaves of the plant are soft, alternate and highly dissected giving a fine feathery appearance. They are bipinnate to tripinnate, aromatic and bright green in color. The leaf segments are narrow and linear which enhances surface area for photosynthesis. The leaves of plant contain glandular trichomes (oil glands) which are responsible for the characteristic apple- like scent.
Fruit and Seed : The fruit of Anthemis nobilis is small, dry cypsela containing single seed. Pappus structure are reduced or absent so that seed can grow primarily on gravity or short- distance movement.
Medicinal Use :
Anthemis nobilis is highly regarded in European herbal traditions. Greeks and Romans use this plant for digestive problems such as indigestion, gas and bloating. It is also used to cure minor wounds, cuts and bruises. Today, Roman chamomile is not only used in folk medicine but also in modern herbalism where it is used for antispasmodic, anti- inflammatory and mild sedatives. It is also used in aromatherapy to reduce stress, anxiety and insomnia.
Causes :
Anthemis nobilis has been used to treat variety of ailments but has some causes also. The plant contains many bioactive compounds which are main causes of its medicinal benefits. In some cases, it can also cause allergic reactions such as rashes on skin, itching or respiratory problem.
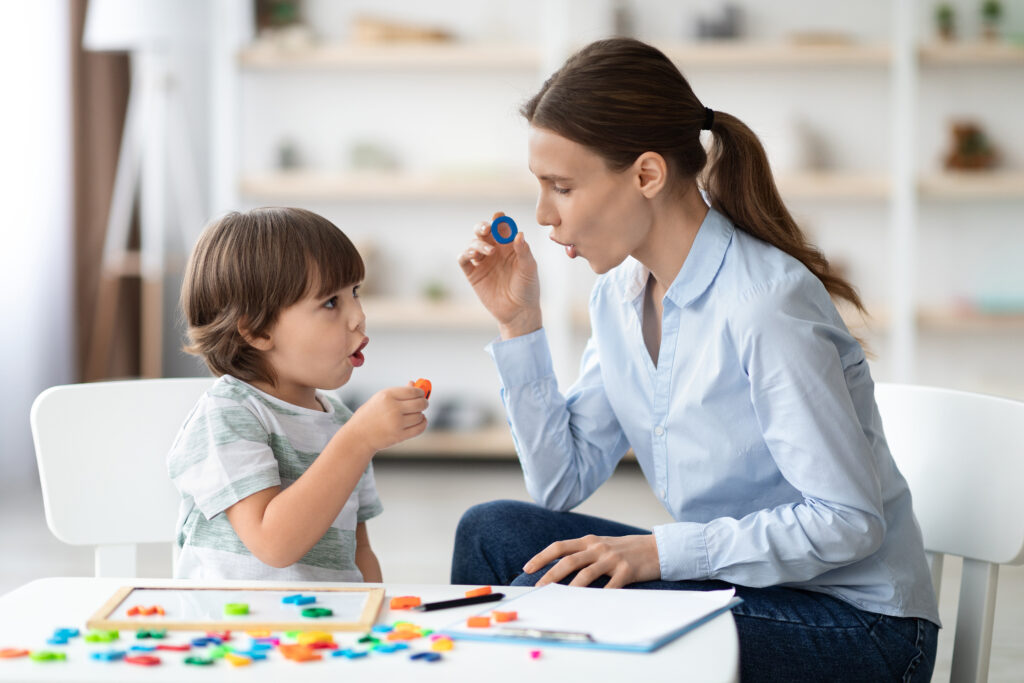
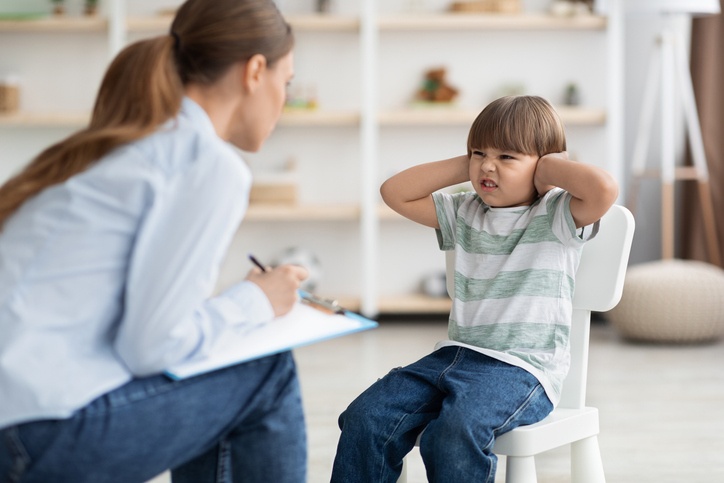
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...