Overview
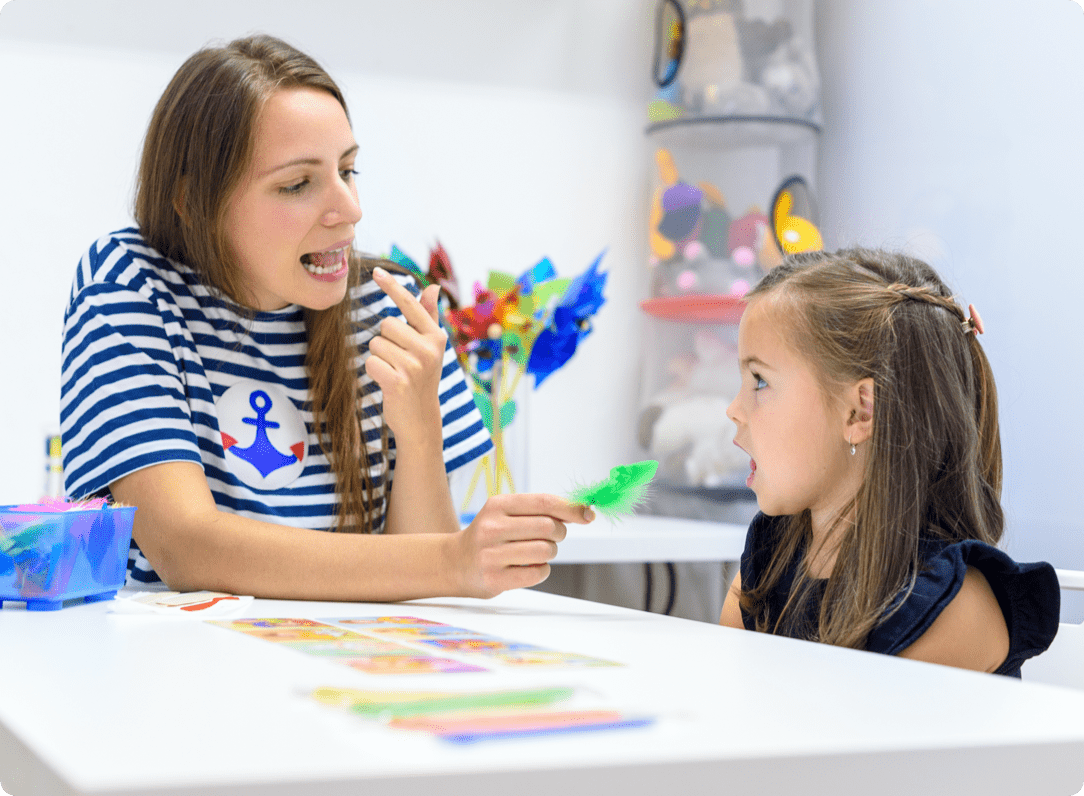
A speech disorder refers to any condition that affects a person's ability to produce speech sounds correctly, speak fluently, or use their voice appropriately. It can involve issues with articulation (pronouncing words correctly), fluency (such as stuttering), voice (problems with pitch, volume, or quality), and resonance (how air flows through the nose and mouth). Individuals with speech disorders may have difficulty being understood, experience tension or anxiety when speaking, or avoid communication altogether. The causes of speech disorders can vary and may include developmental delays, hearing loss, neurological conditions, brain injury, or genetic factors. Treatment often involves speech therapy, which helps individuals improve their ability to communicate effectively and confidently. Early intervention can be crucial in managing and overcoming speech disorders
Symptoms
A speech disorder refers to a condition where a person has difficulty producing speech sounds correctly or fluently, or has problems with their voice. These issues can affect how a person speaks or communicates with others.
There are several types of speech disorders:
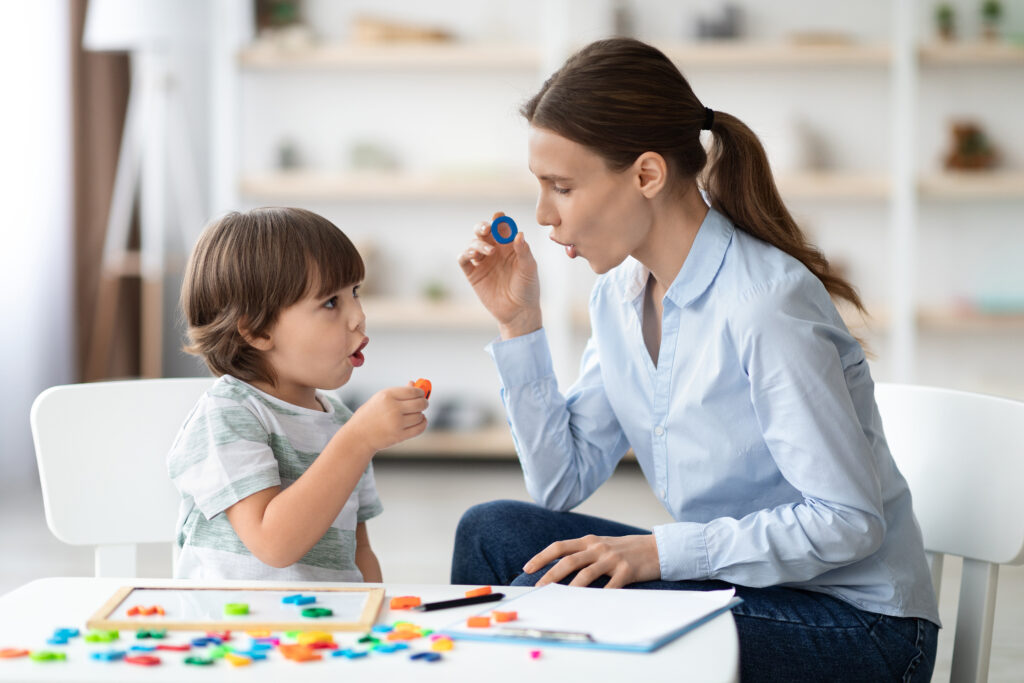
1.Articulation Disorders: Difficulty pronouncing certain sounds correctly. For example, a child may have trouble saying "r" or "s" sounds.
2.Fluency Disorders: Problems with the flow or rhythm of speech, such as stuttering. People with fluency disorders may repeat sounds, syllables, or words, or pause frequently.
3.Voice Disorders: Problems with the pitch, volume, or quality of the voice. For example, a person may sound hoarse or have a very high or low-pitched voice that is not typical for them.
4.Resonance Disorders: When there are issues with the way air flows through the nose or mouth while speaking, often resulting in too much or too little nasal sound in the voice.
5.Other General Symptoms: Difficulty being understood by others, Avoidance of speaking or communication situations, Limited vocabulary or difficulty forming sentences, Speech that is hard to follow or unclear.
Speech disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, such as genetics, hearing loss, developmental delays, brain injuries, or neurological conditions. Treatment often involves speech therapy to help the person improve their ability to communicate effectively.
Causes
The causes of speech disorders can vary widely, and they may be linked to several factors. Common causes include:
1.Genetic Factors: Speech disorders can run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Children may inherit conditions like stuttering or articulation disorders from their parents or relatives.
2.Developmental Delays: Some children may experience delays in speech development, which can result in speech disorders. These delays may be related to general developmental delays or specific language disorders.
3.Hearing Loss: Difficulty hearing can lead to speech disorders, as hearing is essential for learning to speak correctly. Hearing loss can affect speech sound production and the ability to understand language.
4.Brain Injuries or Neurological Conditions: Damage to areas of the brain responsible for speech and language can cause speech disorders. Conditions like cerebral palsy, stroke, or traumatic brain injury can result in difficulties with speech production or motor control.
5.Structural Abnormalities: Physical issues with the speech organs (like the mouth, tongue, teeth, or vocal cords) can cause speech problems. Examples include cleft palate, tongue tie, or other congenital issues.
6.Environmental Factors: Exposure to factors like toxic substances (e.g., lead poisoning) or extreme stress during pregnancy can contribute to the development of speech disorders.
7.Psychological or Emotional Factors: In some cases, psychological issues, such as trauma or anxiety, may cause speech disorders, particularly in children (e.g., selective mutism or stuttering).
8.Language Processing Issues: Some children may have difficulty processing language, which can lead to speech and language disorders. These issues affect their ability to understand and produce spoken language.
Each case is unique, and identifying the cause of a speech disorder often requires a comprehensive evaluation by a speech-language pathologist.
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...