Part Used:
Root
Where It Grows (Habitat):
This plant is a small shrub about 1 foot tall, belonging to the Rubiaceae family. It mostly grows in the moist, shady forests of Brazil, especially in places like Matto Grosso and around the German colony of Philadelphia (north of Rio de Janeiro). It’s also found in New Granada and Bolivia.
Plant Description:
-
It has a thin stem that grows partly underground.
-
The lower part of the stem has knots, from which fibrous roots grow.
-
Some of these roots become thick and store starch in their bark.
-
Only these thickened roots are collected, cleaned, and dried to be used in medicine because they contain the plant's useful substances.
When collected:
The roots are mostly harvested by local people (often by the Indians) during January and February, when the plant is flowering. These roots are called Brazilian or Rio Ipecacuanha in the market.
History & Traditional Uses:
-
A Portuguese friar living in Brazil around 1570–1600 mentioned a root called Ipecaya or Pigaya used for treating bloody diarrhea (dysentery).
-
The root wasn’t known in Europe until 1672, when a traveller named Legros brought it to Paris.
-
By 1680, a Paris merchant named Garnier informed the famous physician Helvetius about its powerful effects in curing dysentery.
-
The exact plant was identified by Dr. Gomez from the Portuguese Navy in 1800.
Substitutes:
Other similar roots like East Indian Ipecacuanha (from a different plant called Cryptocarpus spiralis) have been used, but they are quite different from the true Ipecacuanha in structure and effects.
What It Contains (Constituents):
The main chemicals in Ipecacuanha root are:
-
Emetine (about 72% of the alkaloids)
-
Cephaelin (about 26%)
-
Psychotrine (around 2%)
Other substances include starch, sugar, calcium oxalate crystals, some fats, and a strong-smelling oil.
Note:
-
Emetine is the most important, giving the plant its strong medicinal effects.
-
East Indian Ipecacuanha contains small amounts of different emetic chemicals.
Medicinal Actions & Uses:
-
In Large Doses:
Acts as an emetic (causes vomiting). -
In Smaller Doses:
-
Works as a diaphoretic (makes you sweat).
-
Acts as an expectorant (helps cough out mucus).
-
Stimulates the stomach, intestines, and liver, improving appetite and digestion.
-
-
For Dysentery:
Used for treating amoebic dysentery (a severe type of diarrhea with blood).
However, because it can cause vomiting, special preparations called de-emetized Ipecacuanha (without Emetine) are also used. -
On Skin:
When applied as a powder, it causes irritation and small blisters. -
When Inhaled:
Causes sneezing and slight inflammation of the nasal lining. -
Effects on Lungs and Stomach:
It affects the vagus nerve (pneumogastric nerve), causing irritation in the chest and stomach. -
Other Important Uses:
-
Helps with persistent nausea and vomiting, especially after eating heavy, indigestible foods like cakes, raisins, etc.
-
Beneficial for weak, overweight children or adults who easily catch colds in warm, humid weather.
-
Treats spasmodic (sudden, involuntary) conditions and heavy bleeding (bright-red and profuse).
-
Commonly used in Peptorale group of medicines for respiratory issues.
-
Caution:
Ipecacuanha is a strong medicine and should only be used under the guidance of a qualified doctor, especially because its main component Emetine can affect the heart if taken in large amounts.
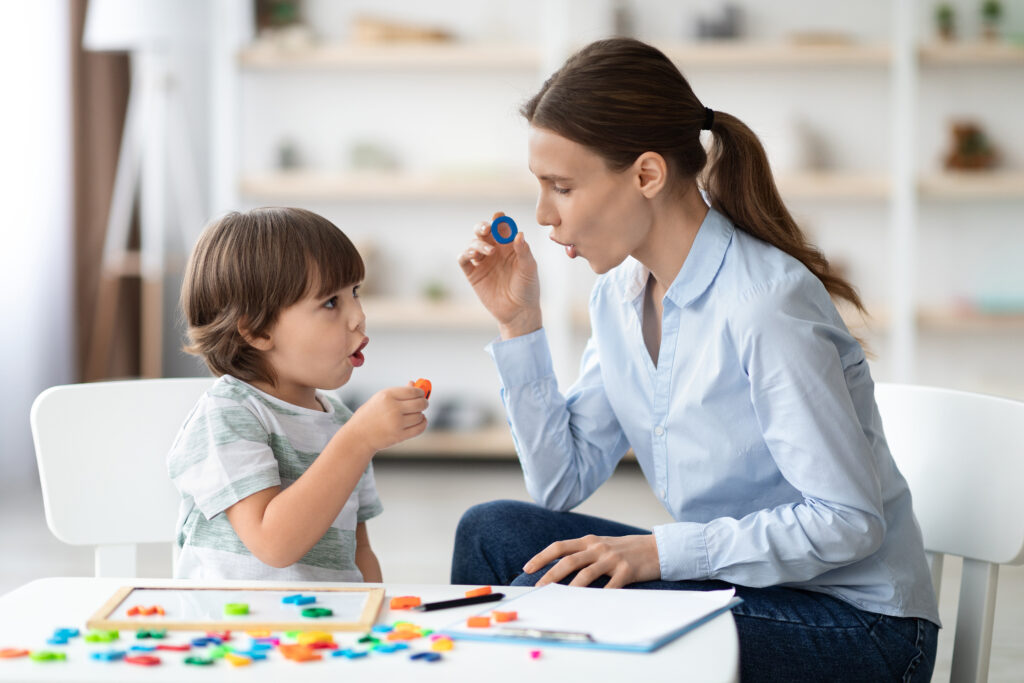
Speech Disorder
A speech disorder, also known as a speech impairment...
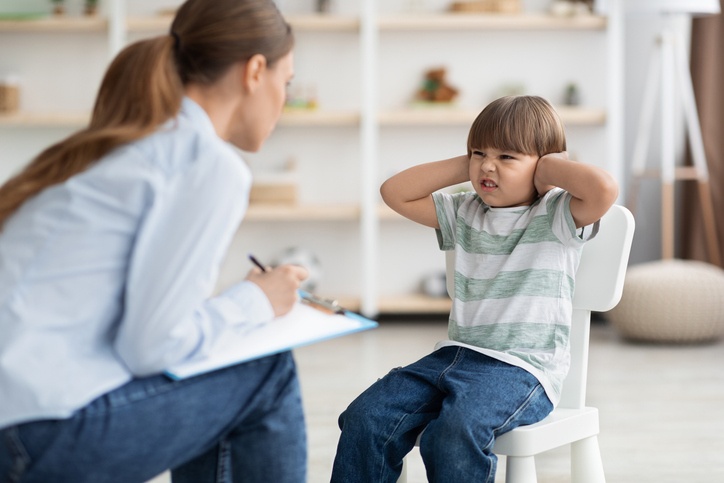
ADHD
Attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a...
Cerebral Palsy(CP)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders...
Cancer
Cancer is a broad term for diseases where cells...